The ankle joint is often injured because it withstands heavy loads. A doctor can diagnose ankle osteoarthritis based on the symptoms and prescribe treatment. The disease is independent of age and gender; the tissue becomes thinner and destroyed, which can lead to disability.
Osteoarthritis affects 12% of residents; women of retirement age are more often affected by the disease.
As already mentioned, the ankle can withstand a tremendous amount of stress. It keeps the body upright and allows a person to move. His injury changes his usual way of life.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle (symptoms and treatment may vary) is a chronic disease in which irreversible processes occur in the cartilage.
The disease progresses gradually. A healthy person has a smooth joint surface. When overloaded, it promotes easy gliding during physical activity.
With osteoarthritis, tissue nutrition and metabolism deteriorate. The outer surface of the joint changes, becomes rough, cartilage is touched and inflammation occurs. When a person lifts heavy objects, the load falls on the bone, which leads to degenerative diseases.
If treatment is not started, serious pathologies develop. In later stages, cartilage and tissue are affected, the synovial lining becomes irritated and the joint loses stability. In this case, the support function suffers and movements become more difficult.
species
Depending on different criteria, there are different types of osteoarthritis:
- Causes of origin (primary, secondary);
- stages of osteoarthritis;
- localization of pathology;
- forms of localization (generalized and local);
- Course of the disease (acute and chronic).
| Classification criteria | Types of osteoarthritis |
|---|---|
| Place of manifestation | Knee, wrist, ankle, elbow, shoulder and neck osteoarthritis. |
| Cause of occurrence |
|
| Localization |
|
| Course of the disease |
|
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is divided into primary (degenerative processes begin in healthy cartilage due to excessive physical activity) and secondary (destruction is diagnosed, dystrophic changes occur in the cartilage tissue).
Stages and degrees
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint (symptoms and treatment directly depend on the patient's age) can occur in various ways. For some, it takes many years from the appearance of the first symptoms to the critical stage, while for others the disease develops quickly.
It depends on the age and the comorbidities at the start of therapy. As ankle osteoarthritis progresses, the symptoms worsen.
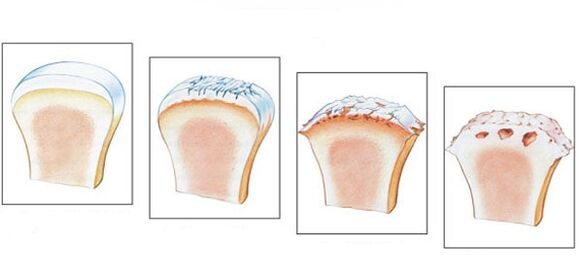
There are 4 stages of the disease.
- The first stage is often ignored. Main symptoms: stiffness that occurs in the morning, characteristic crunching when walking. Pathogenic changes cannot be seen in the image; the destructive process has already begun.
- Morning stiffness lasts longer. The development of the leg takes 20 to 30 minutes. Some patients suffer from lameness. On an x-ray, you can identify stage 2 pathology by bone growth and bone displacement.
- In stage 3, the symptoms worsen. Painful sensations appear in a calm state; the patient cannot do without painkillers. Lameness becomes noticeable and crutches are sometimes necessary. The joint swells, changes, the muscles become thinner and decrease in volume. The joint space narrows, as seen on an x-ray, and osteophytes form.
- The final stage develops without treatment. The cartilage is destroyed and the joint surfaces grow together. The patient cannot walk.
There are different degrees of osteoarthritis:
- First degree– No changes or articulations are visible in the x-ray. There is slight morning stiffness. Treatment must begin at this stage.
- In the second degreeActivity becomes difficult, a crunching sound is heard when walking, swelling is observed. The x-ray shows a reduction in the space between the joints. The person limps and morning stiffness lasts longer.
- In the third degreeclearly pronounced cruciate arthrosis, deformation of the joints. The muscles atrophy even more and movements are restricted. Constant rest is required. Even in this condition the pain does not go away.
- At the last graduationThere is virtually no joint space and activity is almost impossible. X-rays allow you to diagnose a large number of osteophytes. Only surgical intervention is prescribed.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle occurs gradually, so treatment should begin as soon as the first symptoms appear in order to prevent the disease from worsening and complications from occurring.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the ankle is characterized by several symptoms (they affect the treatment method):
- The pain is initially moderate and only occurs with physical activity. Over time, the pain becomes worse and becomes disturbing when resting;
- with injuries and dislocations, swelling and inflammatory manifestations occur, and an increased temperature occurs in the area of the injury;
- "dry" clicking, accompanied by pain;
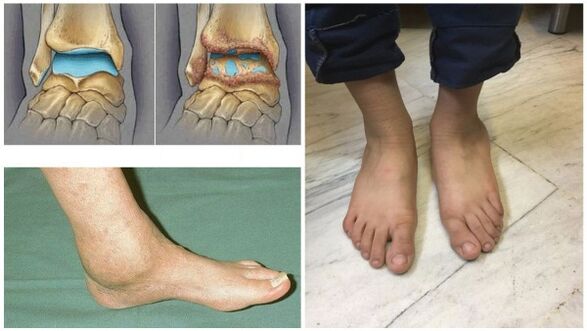
- Dislocation: As the cartilage tissue becomes thinner and broken down, the joint loses stability. The bones are displaced and fall out of the joint capsule;
- joint stiffness;
- when walking, a person quickly gets tired;
- In the final stages, deformation of the joint occurs.
If at least one symptom occurs, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Reasons for appearing
Osteoarthritis of the ankle (symptoms and treatment are often due to age-related changes) affects the older generation. Recently, pathology has been observed in young people.
Provoking factors are:
- Injuries, dislocations and bruises;
- age-related diseases of the joints and ligaments;
- inflammatory processes;
- obesity;
- Violation of metabolic processes;
- congenital foot deformity and flat feet developed throughout life;
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessive physical activity;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- Osteochondrosis.

Less synovial fluid is produced, resulting in less nourishment to the cartilage. The joint space narrows, which can lead to bone fusion. This leads to cruciate arthrosis that cannot be reversed. However, treatment should be prescribed immediately to prevent the disease from progressing.
diagnosis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis consists of examining the symptoms present and data obtained from research. Since there are no tests that can clearly determine the pathology, doctors recognize laboratory methods as insufficiently effective.
During remission, the indicators are normal, during relapse a blood test shows an increased level of ESR and c-reactive protein. This means that the pathology has already begun.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental methods are used:
- SimplyRadiographyis the most reliable method. Muscles do not perceive X-rays equally well: soft muscles transmit them, hard ones absorb them. The study reveals the disease itself and its consequences.
The image allows you to analyze the condition of the bone surfaces in the joint, the shape, size and location of the structures relative to each other, the condition of the tissue and the size of the joint space. Thanks to this data, the degree of pathology can be determined.
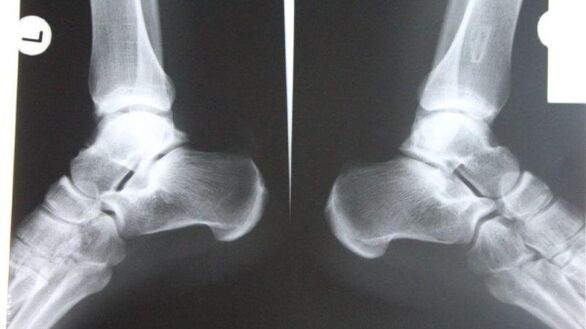
If the ankle joint is affected, the diagnosis is made in the lateral, posterior and posterior projection with the foot moved inward. If there are corresponding symptoms (joint space narrowing, osteophytes and other signs), osteoarthritis is diagnosed.
- Nuclear magnetic resonancedetermines the dysfunction of hydrogen molecules under the influence of a strong magnetic field. Allows exploration of areas of the body that contain water.
The dark tone in the image represents the bones as their water content is much lower and the muscles, nerves and discs appear lighter. Diagnostics reveals even minor diseases of bone tissue and joints. The procedure is indicated before joint replacement. The only disadvantage is the high cost of diagnosis.
- Magnetic resonance imagingExamines very closely the ligamentous structure of the joint, muscle tissue and cartilage. Thanks to the study, a specialist can assess the condition of the lower leg joints, which makes it possible to detect pathologies at the very beginning of their development. The procedure is painless and takes about 30 minutes.
During the procedure, radio waves and strong magnetic radiation affect the person. It must be remembered that the magnetic field is dangerous for the physiological state. MRI is prohibited in neuropsychic disorders, pregnancy and the presence of metal objects in the body.
- Ultrasonicenables an accurate diagnosis. The device creates waves that are reflected from the tissue and recorded on the screen. The doctor examines the image and makes a diagnosis. A gel is used to sharpen the image, removing air and ensuring easy movement across the surface.
The advantages of this procedure are health safety, affordable price and high accuracy.
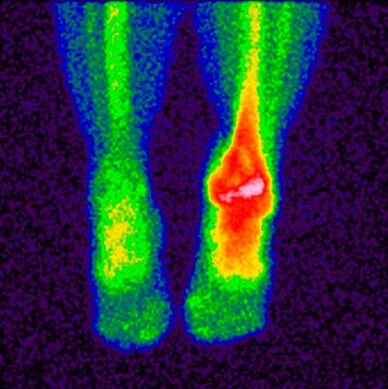
- Bone scintigraphy– a study that makes it possible to determine pathological disorders in bones using isotopes. A special substance containing labeled atoms is injected into the patient's body. Pathological areas are divided into cold and hot.
In the first case, there are no isotopes, blood circulation is worse and they are not detected during scanning. This also includes places where malignant tumors have occurred. In hot areas, isotopes are collected more actively and are clearly detected during scanning. These areas indicate the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
This study makes it possible to distinguish osteoarthritis from similar diseases with similar clinical symptoms; based on the results, the doctor makes a prognosis and prescribes treatment.
The main contraindications to the study are carrying a child, breastfeeding and taking medications containing barium.
- Joint punctureis a procedure in which the doctor inserts a needle into the joint cavity to collect synovial fluid for analysis.
This biomaterial will continue to be studied in the future; Based on the results, the specialist determines the characteristic features of the disease and its stage of development. In the case of ankle arthrosis, a puncture is made in the front part between the outer malleolus and the tendon of the extensor digitorum longus muscle.
When should you see a doctor?
If treatment for osteoarthritis is not started in a timely manner, it will result in inability to work and sometimes even incapacity to work. Some patients are in no hurry to seek help because they don't know which doctor to make an appointment with. At the first symptoms, you need to see a rheumatologist who will diagnose dystrophic and inflammatory changes in the joint.
You should contact him if:
- after excessive stress at the end of the working day, discomfort and pain in the joints occur;
- it is difficult to find a comfortable position for the legs at night;
- Joints swell, skin turns red;
- there is a sharp pain, it is difficult to move;
- Crunching and clicking noises occur;
- Joints are deformed.
With the help of modern diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, it is possible to avoid surgical interventions and preserve the function of the joint.
prevention
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint (symptoms and treatment can be discussed with a doctor) can be prevented.
To prevent arthrosis, experts recommend adhering to certain rules:
- Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes without heels.
- Pay attention to proper nutrition, drink enough clean water;
- Choose a suitable vitamin and mineral complex;
- To do sports;
- Take walks in the fresh air more often.
- Avoid excessive strain on your legs.
- avoid hypothermia;
- be regularly observed by doctors;
- give up bad habits;
- Do a series of exercises to warm up the ankle.

It is particularly important to adjust your diet. Nutritionists have agreed on a menu that will prevent the disease from exacerbating and saturate the body with the necessary substances.
- You need to eat often and in small portions.
- Drink at least 2 liters of clean water.
- Avoid sweet and salty foods.
- Don't eat anything 4 hours before bedtime.
- Steam, bake, cook food.
Fasting and a strict diet for arthrosis are strictly prohibited in order to prevent the leaching of calcium, which is necessary for the restoration of bones and cartilage.
Treatment methods
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment must begin immediately. It is impossible to completely eliminate arthrosis. The main thing is to slow down the destructive processes and prolong the remission period. Various techniques are used for this.
Medication
Various medications are used to treat osteoarthritis:
- Anti-inflammatoryand painkillers eliminate the source of inflammation and relieve pain. Tablets and ointments are used. The sooner anti-inflammatory medications are taken, the greater the chance of saving the joint.
- Glucocorticoidsare used when the above-mentioned medications do not bring the desired result. They are made in the form of an injection solution and injected into the joint.
- Chondroprotectorsnecessary to slow down the process of cartilage destruction.
The treatment regimen and dosage of drugs are determined by the doctor based on the severity of symptoms, concomitant diseases and other factors. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate so as not to aggravate the situation.
Traditional methods
Regarding traditional methods of treating arthrosis, doctors recognize their beneficial properties and positive effects. Traditional medicine is also used to prevent diseases.
The main recipes for treating ankle arthrosis are as follows:
- Burdock leaves are washed thoroughly and applied to the skin with the soft side. The plant is fixed with a bandage or cling film and left overnight.
- Heat sea salt (buckwheat, sand) in a pan, pour it into a linen towel and apply to the sore spot. Hold until the salt gets cold. This is an effective method of pain relief.
- Pour triple cologne over lilacs, leave in a dark place for two weeks and rub the sore spot twice a day.
- Grind eggshells into powder, take 0. 5 tsp. Before the meal.

The use of traditional treatment methods must be coordinated with the treating doctor. This is not the only measure, but an addition to the main therapy.
Other methods
If conservative therapy does not bring any positive effects, they resort to radical measures - surgery.
Indications for surgery are usually:
- recurrent and primary arthrosis of 3-4 degrees;
- complications;
- severe and persistent pain radiating to the knee;
- obvious lameness;
- paralysis of the leg muscles;
- Deterioration of the flexion-extension properties of the joint and the support ability of the foot.
The following surgical procedures are used for arthrosis of the foot:
- Arthrodesis– Surgery to immobilize the joint. Its task is to restore the lost ability to support the limb. The main disadvantage is the risk of bone fusion leading to immobility, which is why it is used very rarely.
- Arthroscopyis a minimally invasive procedure in which the doctor cuts the joint and inserts an arthroscope. The surgeon conducts a visual examination and assesses the condition of the intra-articular structures. If necessary, he removes parts of the damaged joint or blood clots from the synovial fluid. With this operation the risk of recurrence is too high.
- Endoprostheticscarried out in particularly severe cases. Allows partial or complete replacement of a damaged connection. Prostheses with modernized mechanics that last up to 20 years are used.
The main contraindications to surgery are age under 12 years, fistulas in the joint, diabetes mellitus, cardiac dysfunction and infectious diseases.
Possible complications
If treatment is delayed or not received, the following complications may occur:
- Disability;
- deformation that cannot be restored;
- Inactivity and immobility of the joint;
- Deterioration in quality and standards of living.
In addition to these complications, the chronic course of the disease is accompanied by pain, discomfort and the inability to lead an active lifestyle.
To make gymnastics, medication and folk treatments more effective, it is recommended to use special orthopedic aids that reduce the load on the joint. This includes an orthosis and a fixation bandage.
The orthosis completely follows the contours of the ankle, increasing freedom of movement, reducing swelling and pain. The fixation bandage has the same effect as the orthosis. It is made of soft, elastic fabric that allows the joint to be well fixed. The bandage is used only in periods of remission, when the exacerbation has passed.
Osteoarthritis of the ankle is a serious disease that, if left untreated, leads to serious consequences and complete immobility of the joint. Diagnosis at the initial stage, careful attention to symptoms and competent therapy make it possible to avoid surgical intervention.







































